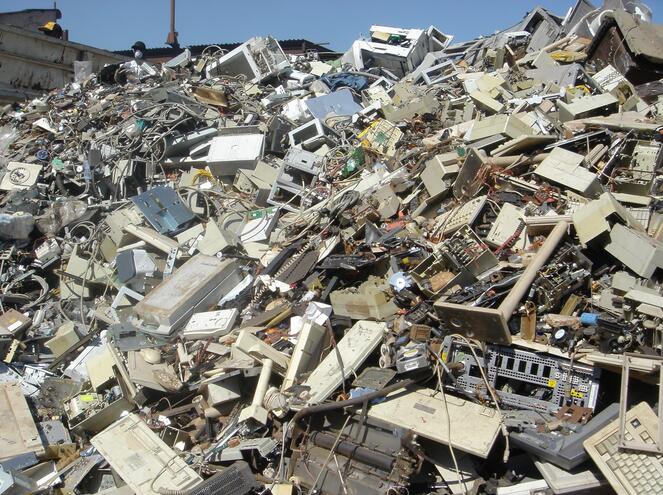
"Electronic waste" or "E-Waste" may be defined as discarded computers, office electronic equipment, entertainment device electronics, mobile phones, television sets, and refrigerators. This includes used electronics which are destined for reuse, resale, salvage, recycling, or disposal. Others are re-usables (working and repairable electronics) and secondary scrap (copper, steel, plastic, etc.) to be "commodities", and reserve the term "waste" for residue or material which is dumped by the buyer rather than recycled, including residue from reuse and recycling operations, because loads of surplus electronics are frequently commingled (good, recyclable, and non-recyclable), several public policy advocates apply the term "e-waste" broadly to all surplus electronics. Cathode ray tubes (CRTs) are considered one of the hardest types to recycle.

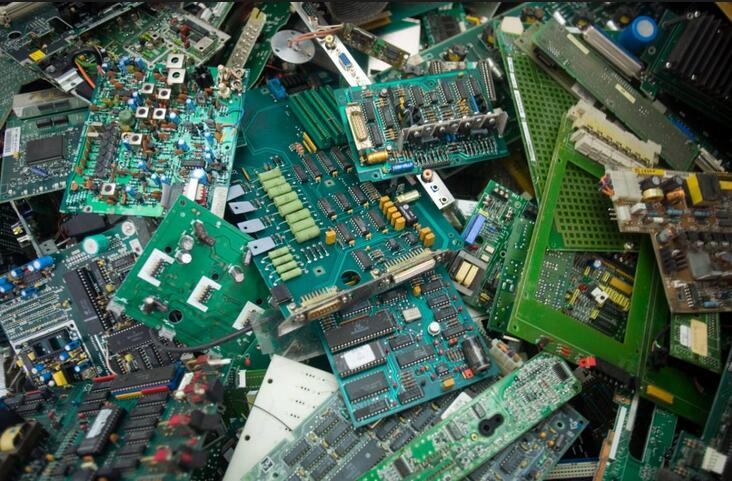
One of the major challenges is recycling the printed circuit boards from the electronic wastes. The circuit boards contain such precious metals as gold, silver, platinum, etc. and such base metals as copper, iron, aluminum, etc. One way e-waste is processed is by melting circuit boards, burning cable sheathing to recover copper wire and open- pit acid leaching for separating metals of value. Conventional method employed is mechanical shredding and separation but the recycling efficiency is low. Alternative methods such as cryogenic decomposition have been studied for printed circuit board recycling and some other methods are still under investigation. Properly disposing of or reusing electronics can help prevent health problems, reduce greenhouse-gas emissions, and create jobs. Reuse and refurbishing offer a more environmentally friendly and socially conscious alternative to downcycling processes.
Recycling raw materials from end-of-life electronics is the most effective solution to the growing e-waste problem. Most electronic devices contain a variety of materials, including metals that can be recovered for future uses. By dismantling and providing reuse possibilities, intact natural resources are conserved and air and water pollution caused by hazardous disposal is avoided. Additionally, recycling reduces the amount of greenhouse gas emissions caused by the manufacturing of new products.]Another benefit of recycling e-waste is that many of the materials can be recycled and re-used again. Materials that can be recycled include "ferrous (iron-based) and non-ferrous metals, glass, and various types of plastic." “Non-ferrous metals, mainly aluminum and copper can all be re-smelted and re-manufactured. Ferrous metals such as steel and iron can be also be re-used. Due to the recent surge in popularity in 3D printing, certain 3D printers have been designed (FDM variety) to produce waste that can be easily recycled which decreases the amount of harmful pollutants in the atmosphere. The excess plastic from these printers that comes out as a byproduct can also be reused to create new 3D printed creations.
Benefits of recycling are extended when responsible recycling methods are used. In the U.S., responsible recycling aims to minimize the dangers to human health and the environment that disposed and dismantled electronics can create. Responsible recycling ensures best management practices of the electronics being recycled, worker health and safety, and consideration for the environment locally and abroad. In Europe, metals that are recycled are returned to companies of origin at a reduced cost. Through a committed recycling system, manufacturers in Japan have been pushed to make their products more sustainable. Since many companies were responsible for the recycling of their own products, this imposed responsibility on manufacturers requiring many to redesign their infrastructure. As a result, manufacturers in Japan have the added option to sell the recycled metals.

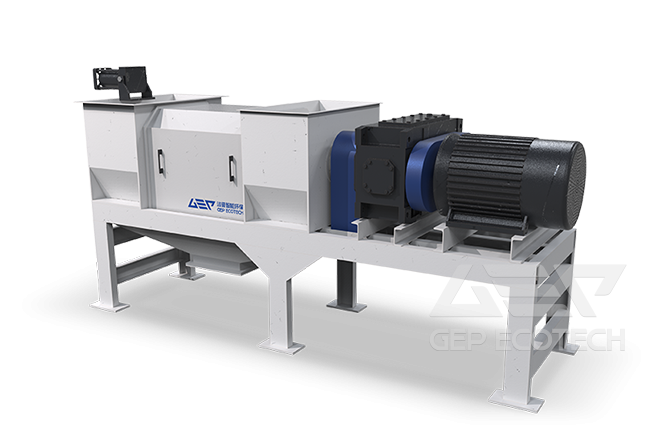
GEP Waste shredder classification
GEP ECOTECH CO., LTD adopt German advance technology, focus on the research, manufacturing, sales and service of intelligent, green technology and solid waste crushing and recycling equipment.
he intelligent solid waste crushing equipment widely used in the field of municipal waste classification and Incineration, cement kiln co-processing, hazardous waste disposal, rubber and plastic waste, electronic waste, organic waste and other solid waste crushing and recycling.
We provide the following shredder:
1. Double shaft primary shredder
GDC series double shaft primary shredder is a new type of shredder which is introduced with German environmental protection technology and combined with GEP independent innovation. Through the innovative design and a lot of practice, GEP shredder has many advantages, such as high breaking capacity, high stability, long life, easy operation, low cost and so on, widely used in various waste disposal industry.
2. Double shaft shearing type shredder
Double shaft shearing type shredder is a new type of shredder which is introduced with German environmental protection technology and combined with GEP independent innovation. Through the innovative design and a lot of practice, GEP shredder has many advantages, such as high breaking capacity, high stability, long life, easy operation, low cost and so on, widely used in various waste disposal industry.
3. Four shaft shearing type shredder
Four shaft shearing type shredder is introduced with German environmental protection technology and combined with GEP independent innovation. Through the innovative design and a lot of practice, GEP shredder has many advantages, such as high breaking capacity, high stability, long life, easy operation, low cost and so on. Four shaft shredder has good adaptability in big size and mixed material crushing, it can adjust the output size accurately by replacing of screen, widely used in various waste disposal industry.
4. Fine shredder
The very sturdy single shaft granulators are suitable for second shredding. Thanks to their construction they are very resistant to foreign objects and can easily treat inhomogeneous materials which are difficult to shred, such as: wood, plastics, waste paper, rubber etc. Fine shredder are suitable, for instance for cement plants and waste to energy plants.